LakeSihwatidalpowerplantproject
- a Daewoo E&C Co., SihwaLakeTidalPowerPlantProject, Ansan 425-330, Republic of Korea
- b Korea Ocean Research & Development Institute, 1270 Sadong, Ansan 426-744, Republic of Korea
- c Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Sungkyunkwan University, 300 Chunchun-dong, Jangan-gu, Suwon 440-746, Republic of Korea
- Received 1 July 2009. Accepted 24 January 2010. Available online 1 February 2010.
1. Introduction
2. Construction of the tidal power plant
3. Hydro-regime update and forecast
4. Conclusion
Acknowledgements
References
Abstract
A TidalPowerPlant (TPP) is being constructed in the middle section of the existing LakeSihwa dike located near the southern Incheon Port in Korea. The project, which will be completed in 2010, is to harness the largest tidal energy in the Kyeonggi Bay in the eastern Yellow Sea. While noting the current progress in terms of plant construction, this paper outlines the overall project in the tidal regime and uses predictive local flow modeling. The results of two-dimensional finite element method simulations that predict the real-time tidal characteristics during the construction and after the completion of the tidalpowerplant are presented, including a method to estimate the electricity output from the plant in the future.
Keywords
- Tidalpowerplant;
- SihwaLake;
- Tidal modeling
Figures and tables from this article:
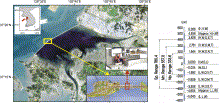
Fig. 1. Location of the Lake Sihwa tidal power plant construction site with tidal datum planes.
- View Within Article
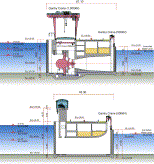
Fig. 2. Schematic of the turbo-generator and sluice gate.
- View Within Article

Fig. 3. A perspective view of the plant after completion.
- View Within Article

Fig. 4. Work procedure of the major construction stage (1) before construction, (2) silt protection, (3) cofferdam and diversion roads construction, (4) dewatering, (5) excavation for drywork, (6) Gantry Crane for temporary wharf*, (7) transport of turbo-generator*, (8) installation of turbo-generator, (9) construction of road over sluice gates, (10) detachment of diversion roads, (11) removal of cellular cofferdam, (12) operational test of turbo-generator. (*This original plan was changed to use special carrier to transport machineries between erection bay and crane sites.)
- View Within Article

Fig. 5. Photograph showing the construction progress of Sihwa tidal power plant.
- View Within Article
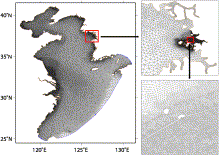
Fig. 6. Mesh of the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea continental shelf (YS) model.
- View Within Article
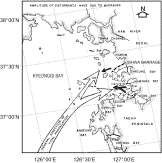
Fig. 7. Amplitude of disturbance waves due to the barrages.
- View Within Article
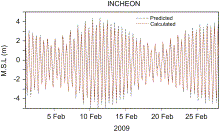
Fig. 8. Comparison of measured and simulated water levels at the Incheon Port.
- View Within Article
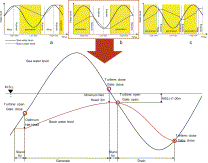
Fig. 9. Three types of tidal power generation: (a) single effect operation (ebb), (b) single effect operation (flood) and (c) double effect operation. Also, a detailed diagram of a single effect operation (flood) for the Sihwa TPP.
- View Within Article
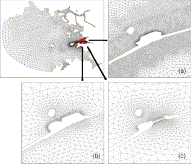
Fig. 10. FEM mesh (a) at the cellular cofferdam for Sihwa tidal power generation on December 2005, (b) on January 2007 and (c) at completed construction.
- View Within Article

Fig. 11. Snapshot of the tidal flow of the cellular cofferdam construction site.
- View Within Article

Fig. 12. Snapshot of the flow velocity at the Sihwa tidal power generation plant during discharging (left) and generation (right)
- View Within Article
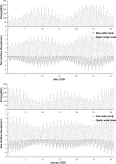
Fig. 13. Computed energy (up) and water level (down) at sea side (dashed line) and basin side (dotted).
- View Within Article
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.